Financial planning for beginners is something I genuinely thought only people with trust funds or CPAs needed—turns out regular broke-ass humans like me need it way more.
I’m sitting here in my apartment outside Philly (well, technically the shitty edge of it), January 2026, heat’s kinda working but not really, and I’m staring at a bank app that’s showing me $312 until next payday while DoorDash is already texting me “We miss you 👀”. Classic.
Why I Sucked at Financial Planning for Beginners (Very Embarrassing Edition)
Three years ago I was 27, making decent money bartending + freelance graphic design, and somehow still always negative. I had:
- $8,400 in credit card debt
- a “fun” wardrobe I couldn’t afford
- approximately zero clue what a 401(k) even did
My lowest moment? Venmo-requesting my mom $40 for gas… at 27… while wearing $120 sneakers I bought on Afterpay. Yeah.
So I decided to try financial planning. The simple version. Not Dave Ramsey screaming at me, not some 47-step Excel nightmare—just basic shit I could maybe stick to.

Step 1: Look at the Damage (aka The Panic Attack That Helped)
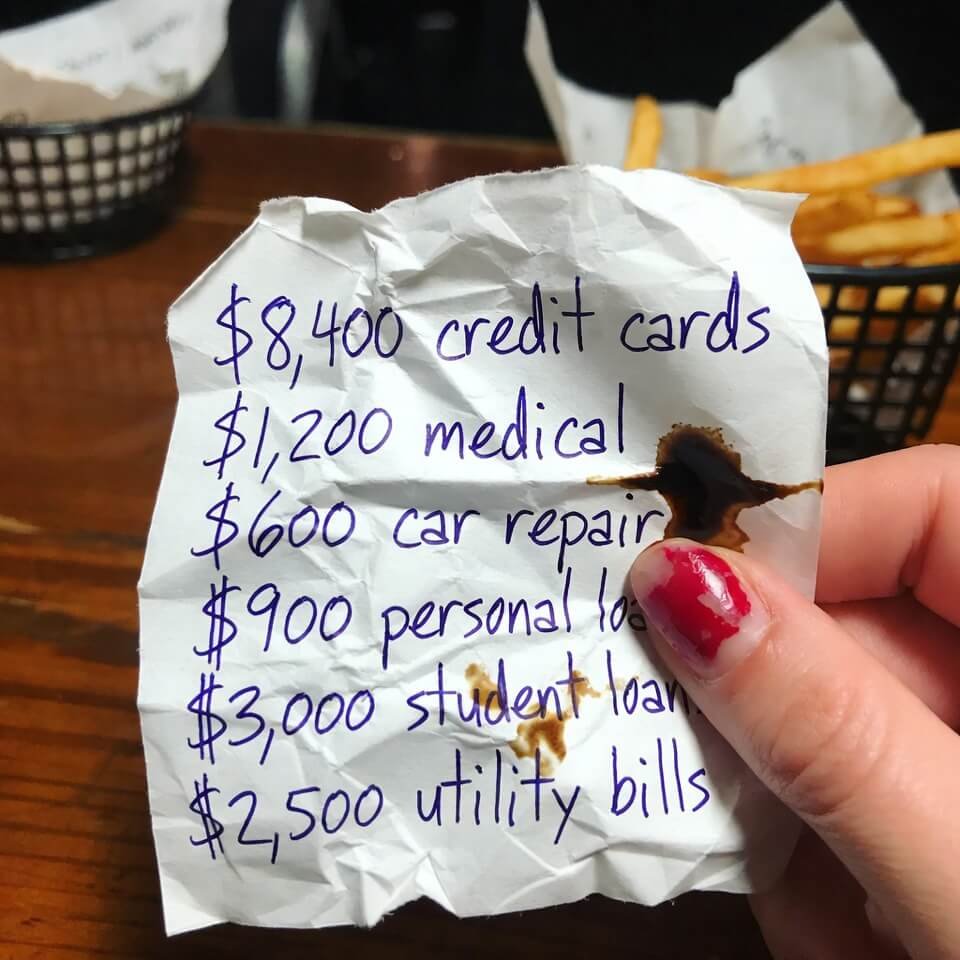
First thing I did was actually open every banking app, credit card login, PayPal, Cash App, Venmo… everything. I almost threw up.
But weirdly, once I wrote the real numbers down (on an actual napkin because my notes app felt too official), the panic dialed back a little.
Pro tip nobody tells you: seeing $9,812.47 in total debt feels less scary once it’s just ink on a bar napkin next to cold french fries.
[Insert Image Placeholder 1] Personal perspective photo: extreme close-up of a napkin with messy blue-pen handwriting showing debt totals, coffee stain in the corner, my chipped nail polish thumb holding it down, shot from above with shaky iPhone focus.
Step 2: The “No BS” Budget That Actually Stuck
I tried zero-based budgeting. Hated it. Felt like I was on house arrest.
Then I tried the 50/30/20 thing everyone recommends. Also hated it—because my “wants” were apparently 65% of my income.
So I made up my own ugly version:
- 60% → must-pay-or-I-die (rent, utilities, minimum debt payments, cheap groceries)
- 15% → debt snowball (extra toward smallest balance first because psychology > math sometimes)
- 10% → emergency fund (yes, I started at $20 a paycheck—laugh at me, it’s fine)
- 15% → literally whatever (fun, eating out, dumb candles, whatever stopped me from rage-quitting)
It’s not elegant. It’s not optimal. But I’ve stuck with it for 14 months now and actually have $2,100 in savings for the first time in my adult life.
Step 3: Tools I Use (Cheap or Free Because I’m Still Cheap)
- Mint or YNAB → I flip between them. Mint is free and passive; YNAB is better but $99/year hurts so I just pirate the mindset from Reddit threads.
- Ally Bank online savings → 3.6% APY right now (as of Jan 2026). Way better than the 0.01% my old bank gave me.
- Acorns → rounds up purchases and invests the change. I have $187 in there from buying too much oat milk latte.
For a solid, beginner-friendly explanation of why high-yield savings matter right now: → Check out NerdWallet’s current best high-yield savings rates
Step 4: The Stuff I Still Suck At (Honesty Corner)
I still eat out too much. I still buy $9 lattes when I’m anxious. I still haven’t maxed my Roth IRA (I put $50/month in and feel proud even though it’s pathetic).
But I’m not pretending to be perfect. That’s the only reason I’m still doing it.
Financial planning for beginners isn’t about becoming a millionaire by Tuesday. It’s about not crying when the car inspection is $400 and you’re not totally sure you’re going to eat next week.

Final Ramble & What I’d Tell 2023 Me
If you’re reading this while eating ramen and panicking about rent, hi, same. Start stupidly small. Write the ugly numbers down. Move $10 a week somewhere safe. Screw up publicly (like I’m doing right now).
You don’t need to be good at math. You just need to be slightly less bad at money than you were last month.
Wanna tell me your most embarrassing money mistake in the comments? I’ll go first: I once Venmo’d my dealer $420 for “pizza” at 3 a.m. and then disputed the charge. He texted me “really bro?”. I deserved that.
Anyway. Start where you stand. Even if where you stand smells like spilled LaCroix and despair.
Love, a hot mess who’s slightly less broke than last year











































